For humans and animals, many aspects of normal behavior and physiology rely on the proper functioning of the body’s circadian clocks.
‘Fight or flight’ – unless internal clocks are disrupted, study in mice shows


For humans and animals, many aspects of normal behavior and physiology rely on the proper functioning of the body’s circadian clocks.

Alzheimer’s dementia predicted by brain amyloid levels, age

Research indicates problematic marijuana use is correlated with poorer COVID-19 outcomes

The Brain & Behavior Research Foundation (BBRF) has announced the winners of its 2021 Klerman and Freedman Prizes, which recognize exceptional clinical and basic research in mental illness. The prizes are awarded annually to honor the work of outstanding scientists who have been supported by the Foundation’s Young Investigator Grants Program. “The Klerman and Freedman prizes […]
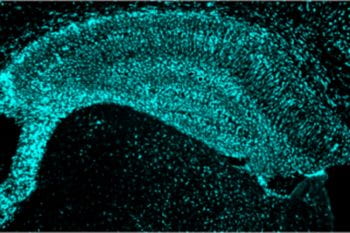
Brain protein reduces Alzheimer’s-like brain damage in mice
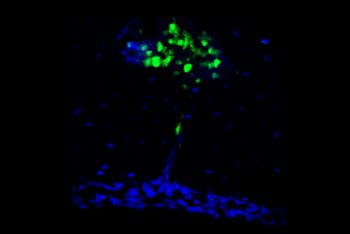
Immune cells from skull bone marrow guard the brain, spinal cord

Tom Burris, Ph.D., FAAAS, FAHA, Alumni Chair in Pharmaceutical Education and vice president for research at University of Health Sciences and Pharmacy in St. Louis, has received a $150,000 grant from the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis’ Philip and Sima Needleman Center for Autophagy Therapeutics and Research to support research related to […]
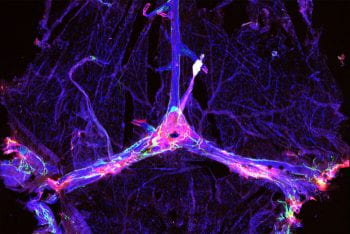
Impaired drainage also may play a role in Alzheimer’s in people
Further studies underway to determine extent of clinical benefits
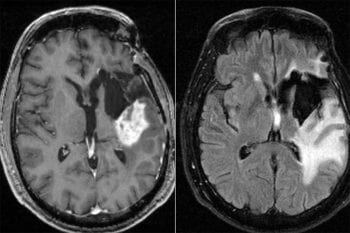
Study indicates timing of chemotherapy could improve treatment for deadly brain cancer