The blood-brain barrier, the body’s way of shielding sensitive brain tissue from viruses, toxins and other harmful substances in the blood, can pose a problem for physicians caring for patients with suspected brain diseases such as cancer. Molecular and genetic information would be invaluable for confirming a diagnosis and guiding treatment decisions, but such molecules are normally confined to the brain by the barrier. Neurosurgeons routinely perform surgical brain biopsies to obtain this data on brain tumors, but such procedures carry risks and are not feasible for all tumors or for many other kinds of brain diseases.
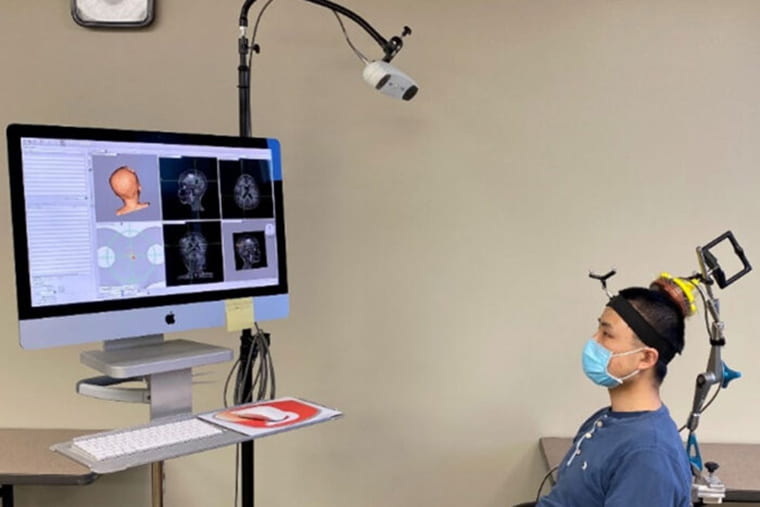
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have developed an anatomically precise technique called sonobiopsy that uses ultrasound and microbubbles to disrupt the barrier temporarily and allow RNA, DNA and proteins from the brain to spill out into the blood, where they can be detected and analyzed. The researchers developed and previously tested the technique in animals. In a new study, available online in the journal NPJ Precision Oncology, they showed that the technique is feasible and safe for use in people, and could open the door to noninvasive biopsies for suspected brain tumors and other brain diseases.
“Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revolutionized the field of brain disease diagnosis in the 1980s and ‘90s by allowing for structural and functional imaging of the brain,” said Eric C. Leuthardt, MD, the co-senior author on the paper and co-inventor of the technology. Leuthardt is the Shi Hui Huang Professor of Neurosurgery and a professor of neuroscience at the School of Medicine and a professor of biomedical engineering and of mechanical engineering at the McKelvey School of Engineering. “Sonobiopsy is the third revolution, the molecular revolution. With this technique, we can obtain a blood sample that reflects the gene expression and the molecular features at the site of a lesion in the brain. It’s like doing a brain biopsy without the dangers of brain surgery.”
The technique was pioneered by Leuthardt and Hong Chen, PhD, an associate professor of biomedical engineering at McKelvey Engineering and of neurosurgery at the School of Medicine. Leuthardt is the director and Chen a member of the Division of Neurotechnology in the Department of Neurosurgery, which focuses on intensely multidisciplinary research to create innovative engineered solutions that can be translated to patients with neurologic diseases. Washington University owns a patent on the sonobiopsy technology.
The procedure works by using focused ultrasound to target a lesion in the brain with millimeter-scale accuracy, followed by the injection of microbubbles into the bloodstream. The microbubbles travel to the targeted spot and then pop, tearing tiny holes in the blood-brain barrier that close within a few hours, leaving no lasting damage. That window of time is long enough for biomolecules from the lesion to escape into the blood, where they can be collected with an ordinary blood draw.
“We’ve essentially initiated a new field of study for brain conditions,” said Chen, the other co-senior author on the paper and co-inventor of the technology. “With this capability to noninvasively, nondestructively access every part of the brain, we can get genetic information on tumors before going in surgically, which would help a neurosurgeon determine how best to approach the surgery. If they see something suspicious on imaging, they could confirm whether a tumor is recurring or not. We can now start to interrogate diseases for which surgical biopsies aren’t done, such as neurodevelopmental, neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders.”